
Currently, active aging and the creation of policies for social participation and health protection for older adults are some of the central issues in the debates on aging.
As part of this, different activities have been developed for older people that, far from being a series of exercises specifically for the elderly, are activities already known but adapted to the needs of this life cycle.
In this sense, the socio-educational process related to active aging can only be carried out if it is based on collaboration, participation and detection of the needs of the elderly themselves. That is, considering his baggage of experiences, his concerns, life stories and personal biography.

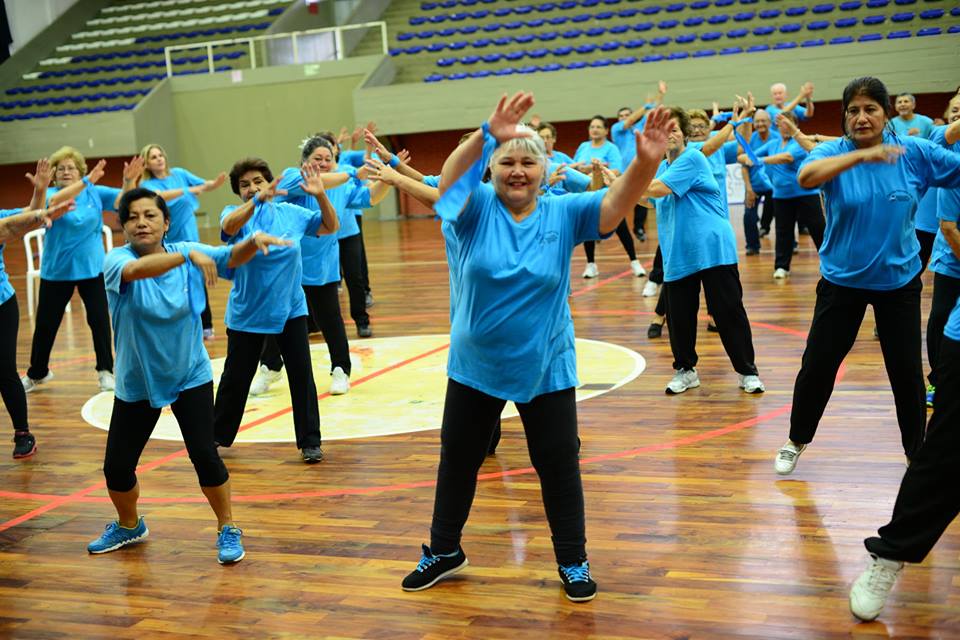
One of the important aspects is to procure physical well-being. This can be favored from two main areas: nutrition and physical exercise. In the case of physical exercise, the activities have the objective of favoring dynamic states of energy and vitality, which help the person to carry out the usual daily tasks, as well as enjoy an active leisure, face excessive fatigue and finally prevent the development of diseases related to sedentary lifestyle.
The activities can be developed to favor the following elements: cardiorespiratory endurance, muscular endurance, flexibility and balance, motor coordination, body composition, among others. To work this there are many activities, for example:
- Rhythmic gymnastics.
- Relaxation and stretching techniques.
- Sports like basketball or volleyball.
- Expressive rhythmic activities such as dance.
- Outdoor work such as aerobics or pilates.
- Swimming with joint mobility exercises.
- Emotional psychic-cognitive well-being
This item includes a series of strategies to favor cerebral plasticity and cognitive functions.
- Teaching of relaxation.
- Training attention and concentration, through selection of relevant information (selective attention), or, perform more than one task simultaneously (divided attention) and finally activities that require long periods of concentration (sustained attention).
- Exercises of abstract reasoning and verbal fluency.
- Tasks of categorization, ordering and classification of information.
- Activities to solve problems at different levels of difficulty.
- Activities that favor curiosity and creativity.

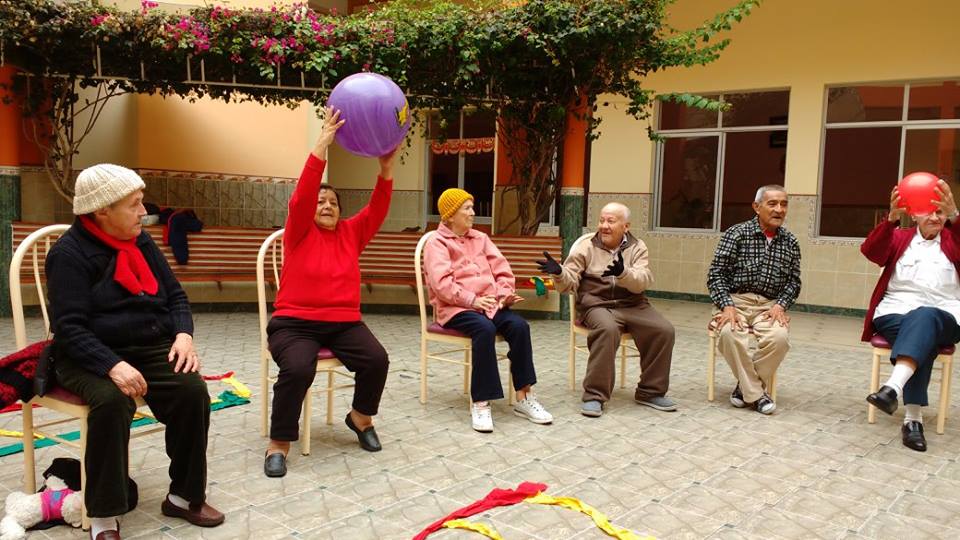
Socio-relational well-being
These activities have the objective of favoring cordial relations, maintaining social contact and increasing interpersonal links. They help to counteract feelings of loneliness and to prevent discomforts related to this life cycle. They can also strengthen socioadaptive skills.
- Encourage the creation of groups of belonging according to common interests, and perform board games or other leisure and recreation activities.
- Practical cooking workshops, which includes the distribution of tasks for planning menus and shopping at nearby stores.
- Group visits to stores or exhibitions.









Leave a reply