
The infection of the urinary tract is an inflammatory process that appears by the multiplication of microorganisms in that area. It can be classified into two types, taking into account its anatomical location, that is, whether it occurs in the lower tracts (urethritis, cystitis and prostatitis) or in the high ones (acute pyelonephritis).
In addition, there are different categories according to the age and gender of the patient. Among elderly people, asymptomatic bacteriuria is the most common and consists of the presence of bacteria in the urine. It occurs to a greater degree in women than in men. The reasons may be in the changes in the vaginal flora due to the decrease in estrogen levels after menopause. Prostatic growth is a common factor of infection in the elderly man and acute urinary retention can trigger infection.
The immune system of the elderly is weaker and they can suffer other diseases that make them more prone to a urinary infection. Among these are dementia (Alzheimer’s), Parkinson’s and central nervous system lesions (neurogenic bladder), urinary and fecal incontinence, diabetes mellitus, catheterization of the urinary tract … In addition, the infection can decompensate some other disease such as diabetes or arterial hypertension. And there are other risk factors such as bladder catheter, uropathy, previous antibiotic therapy or recent hospitalization.
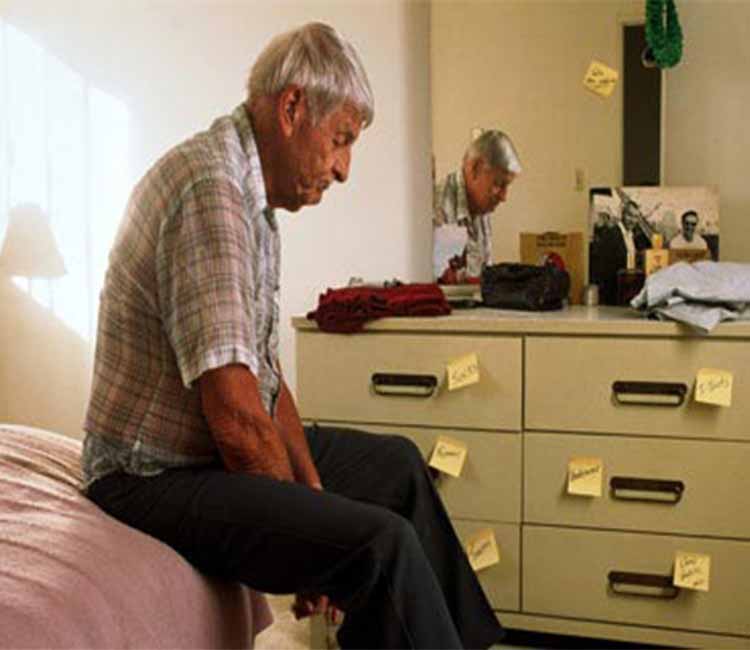

Elderly people may show external signs in their habitual behavior that help diagnose a urinary infection:
- Restlessness
- Irritability
- Decay
- Confusion
- Disorientation
- Tiredness when performing daily tasks.
It can produce fever, hypotension, nausea or vomiting and tachycardia. In general, urinary tract infection is not a serious pathology but in Bastón de Oro we take the quality of life of our residents very seriously and therefore we do our best to detect it in time.
As with many other minor illnesses, maintaining a series of good habits contributes to their prevention. To avoid urinary tract infection, the elderly person should drink frequently, even if they do not feel thirsty. It is convenient to provide them with access to the drink at any time. The goal is to achieve good hydration to make urine less concentrated and eliminate bacteria with frequent urination.
The number of times the bathroom is visited also has an influence: it is necessary to avoid holding the urine in the bladder longer than necessary to avoid the proliferation of bacteria. So, you have to remind them every so often if they feel like urinating. Constipation can also affect this point so, in general, we try to maintain a certain level of physical activity with walks or changes of posture to help mobility.
Hygiene is another determining factor to avoid the risk of urinary infection in the elderly. Women should be specifically cleaned from front to back to avoid passing fecal flora to the periurethral area. In addition to being cleaned with water in the daily toilet, wet wipes can be used when urinating. In case of incontinence, we change the diaper frequently and if it were probes we always handle them with extreme care avoiding unnecessary manipulations.
Leave a reply








Leave a reply